June is Brain Injury Awareness Month, an opportunity to bring attention to the many forms brain injuries can take, as well as the medical tools that can help detect and monitor them.
Brain injuries can be caused by a range of factors, including head trauma, stroke, infection, tumors, or lack of oxygen to the brain. Their effects range widely from person to person, varying from mild symptoms to significant impacts on cognitive, motor, or emotional functions.
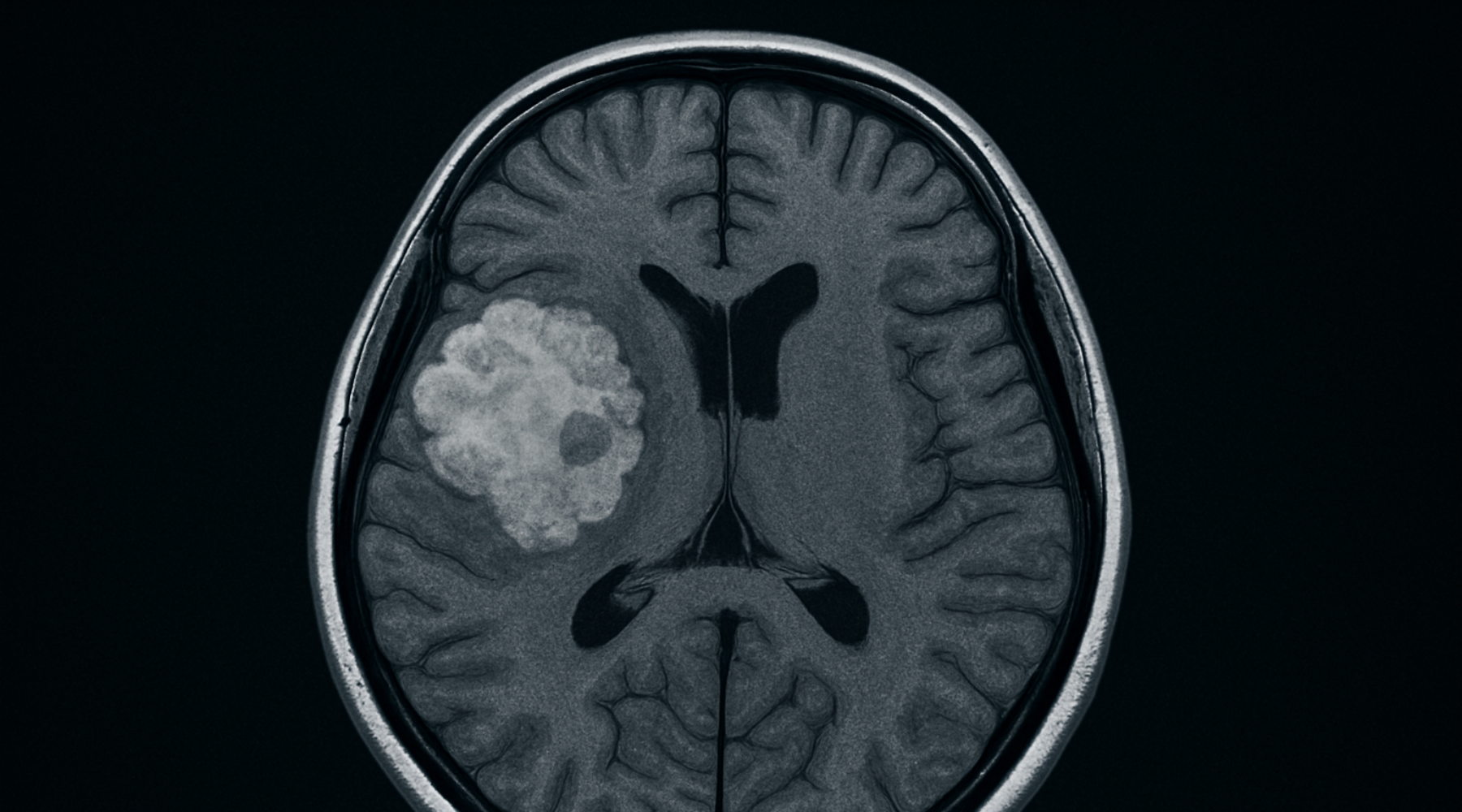
Depending on patient symptoms and condition, brain evaluation may involve a number of different tests. Among these, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become an essential tool over recent decades. Initially focused on visualizing anatomical structures and detecting visible problems such as tumors, bleeding, or stroke, MRI has evolved to include advanced techniques—such as functional and quantitative MRI—that provide even more detailed information about both the structure and function of the brain. These advances give healthcare professionals richer data to support their clinical decisions, enabling a more holistic approach to each patient.
MRI: A Key Test for Brain Assessment
Brain MRI is a non-invasive examination that delivers detailed images of brain structures without radiation exposure. It is commonly used to:
- Visualize the effects of head injuries, bleeding, or swelling
- Identify abnormalities linked to conditions such as tumors or stroke
- Monitor the progress of various neurological conditions
Quantitative Brain MRI: A Valuable Complement for Clinical Needs
Quantitative MRI enables precise analysis of the volume and shape of specific brain regions. This method is especially helpful to:
- Evaluate memory disorders and dementias by measuring hippocampal atrophy and other affected areas
- Monitor multiple sclerosis (MS) by documenting brain changes linked to inflammation
- Track post-stroke effects to optimize rehabilitation
- Analyze the impacts of repeated concussions, especially in contact sports athletes
- Study the neurological impacts of post-traumatic stress (PTSD) in some contexts
These additional data, gathered alongside conventional MRI, can help professionals better understand certain conditions as part of a comprehensive, personalized evaluation.
Radiméd Expertise Supporting Your Health
At Radiméd, our radiologists specialized in neurological imaging bring meticulous attention to every exam. They provide clear, detailed reports to support medical teams in their decision-making, using advanced technologies in a safe and respectful environment.
If you have a referral from your doctor and would like to book an appointment, click here.
Note: MRI—whether conventional or quantitative—is one assessment tool among others and does not replace clinical examination or personalized medical follow-up. Only a healthcare professional can determine whether this exam is appropriate for you based on your clinical context.